|
General
Bones and Joints
The bones of the shoulder:
 The
humerus is the upper arm bone. This is the
"ball" of the shoulder's "ball and socket" joint. The
humerus is the upper arm bone. This is the
"ball" of the shoulder's "ball and socket" joint.
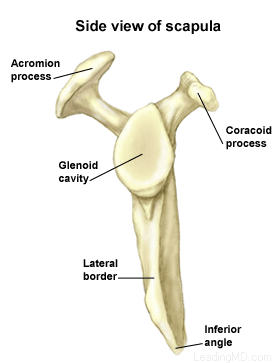
- The scapula
is the flat, triangular bone commonly called the shoulder
blade. Prominent areas of the scapula serve as attachment
points for many muscles and ligaments.
- The glenoid is
the shallow "socket" on the side of the scapula that receives
the 'ball' of the humerus. Together they form the "ball
and socket" arrangement of the shoulder.
- The scapular spine
is a horizontal ridge along the back of the scapula that
divides the scapula into upper and lower regions.
- The acromion is
the end of the scapular spine. It projects up to form the
top of the shoulder.
- The coracoid process
is a projection towards the front of the scapula and is
an attachment site for several muscles and ligaments.
- The clavicle
is the collarbone. Although it appears to be straight, it
actually forms an S-shape when seen from above.
- The thorax,
or rib cage, is an anchor for several muscles and ligaments.
Although the ribs do not physically attach to the scapula,
the thorax stabilizes and maintains proper positioning of
the scapula so that the arm can function to its fullest
capacity.
Additionally, there are four bone
junctions, or joints:
- The glenohumeral joint
is the main joint of the shoulder. Here, the glenoid
on the scapula and the head of the humerus
come together. The fairly flat socket of the glenoid surrounds
only 20% - 30% of the humeral head. Because of its poor
fit, this joint relies heavily on the surrounding soft tissue
for support. The labrum, a ring of fibrocartilage
tissue, attaches to the glenoid and deepens the socket to
encircle more of the humerus.
- The acromioclavicular
joint, or AC joint, is the bony point on the top
of the shoulder. It stabilizes the scapula to the chest,
by connecting the acromion on the scapula
to the clavicle, or "collarbone". A thick
disk of fibrocartilage acts as a shock absorber between
the two bones. The surrounding capsule and ligaments give
this joint great stability.
- The sternoclavicular
joint, or SC joint, connects the other end of the
clavicle to the sternum, or
"breastbone". Like the AC joint, this joint contains a fibrocartilage
disk that helps the bones achieve a better fit. It also
gets excellent support from its joint capsule and surrounding
ligaments.
- The scapulothoracic
articulation is the area where the scapula,
embedded in muscle, glides over the thoracic rib cage.
The surrounding muscles and ligaments keep the scapula properly
positioned so that the arm can move correctly.
Cartilage
There are two types of cartilage in the shoulder:
- Articular cartilage
is the shiny white coating that covers the
end of the humeral head and lines the inside surface of
the glenoid. It has two purposes:
- To provide a smooth, slick surface
for easy movement
- To be a shock absorber and protect
the underlying bone
- Fibrocartilage
is the thick tissue that forms the disks of
the AC and SC joints and the labrum, the ring
that deepens the glenoid. Fibrocartilage has three roles:
- To act as a cushion in shock
absorption
- To help stabilize the joint by
improving the fit of the bones
- To act as a spacer and improve
contact between the articular cartilage surfaces
Ligaments
The
shoulder relies heavily on ligaments for support. Ligaments attach bone to bone and provide the"static" stability
in a joint. Ligaments will alternately become tight and loose
with normal motion. They keep the joint within the normal limits of
movement.
- The glenohumeral ligaments
attach in layers from the glenoid labrum to form the joint
capsule around the head of the humerus.
- The coracoacromial
arch is the group of ligaments that spans the bony
projections of the coracoid process and the acromion.
- The coracoclavicular
ligaments and the acromioclavicular ligament
provide most of the support for the AC joint.
Muscles and Tendons
Muscles and tendons work together in the shoulder to provide
the "dynamic" stability of the shoulder.
There are four muscle groups in the shoulder:
- The rotator cuff muscles
are the subscapularis, the supraspinatus,
the infraspinatus, and the teres minor.
They are the primary stabilizers that hold the "ball" of
the humerus to the glenoid "socket". The socket is too shallow
to offer much security for the humerus. These four muscles
form a "cuff" around the humeral head, securing it firmly
in the socket. As its name implies, this group of muscles
also rotates the arm. The rotator cuff protects the glenohumeral
joint from dislocation, allowing the large muscles that
control the shoulder to power the arm with great mobility.
- The biceps tendon complex
also helps keep the humeral head in the glenoid and helps
raise the arm.
- The scapulothoracic
muscles attach the scapula to the thorax. Their
main function is to stabilize the scapula to allow for proper
shoulder motion.
- The superficial muscles
of the shoulder are the large, powerful outer layer of muscles
that are important to the overall function of the shoulder.
This group includes the deltoid muscle, which
covers the rotator cuff muscles.
Bursae
A bursa is a pillow-like sac filled with a small amount
of fluid. Bursae (plural) reduce friction and allow smooth gliding
between two firm structures, like bone and tendon or bone and
muscle. There are over 50 bursae in the human body; the largest
is the subacromial bursa (under the acromion) in the
shoulder. The subacromial bursa and the subdeltoid bursa (under
the deltoid muscle) are often considered as one structure. This
bursa separates the rotator cuff and the deltoid muscle, from
the acromion. |








 The
humerus is the upper arm bone. This is the
"ball" of the shoulder's "ball and socket" joint.
The
humerus is the upper arm bone. This is the
"ball" of the shoulder's "ball and socket" joint.