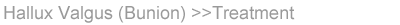
How is a bunion treated?
Non-Operative Treatment
As a general rule, a bunion does not require any treatment other
than a soft shoe with plenty of room for the front of the foot.
- A wide toe box will provide protection for the affected area.
- Shoes that have a seam or lace that crosses the bunion area
should not be worn.
- A soft arch support or a sling may take pressure off the second
toe.
Operative Treatment
Surgery may be necessary if the patient has a severe deformity that
causes constant pain, a dislocation of the second metatarsophalangeal
joint (at the base of the great toe), or hammer toes. Bunion surgery
should be chosen only when conservative treatment has failed. It should
never be performed for cosmetic reasons.
There are many surgical procedures for the treatment of bunions. The
severity of the condition will determine which operation is chosen.
The surgery is usually performed with a local anesthetic block, and
as a rule does not require an overnight hospital stay.
The Chevron Procedure
The chevron procedure is generally used to treat a large
bunion deformity in which there is minimal angulation of the great
toe. A "V", or chevron shaped cut, is made near the end of the
bone, which allows the surgeon to slide the head of the bone laterally,
or toward the little toe. This produces some narrowing of the foot,
and at the same time, some correction of a mild bunion deformity.
The Distal Soft Tissue Procedure and Proximal Metatarsal Osteotomy
A distal soft tissue procedure and proximal metatarsal osteotomy
is the most commonly performed operation. In this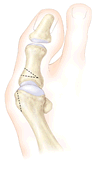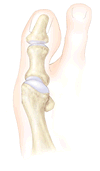 procedure the metatarsolphalangeal
joint is realigned by: procedure the metatarsolphalangeal
joint is realigned by:
- releasing the contracted tissue on the lateral
(little toe) side of the joint.
- shaving off the large bunion on the medial (great
toe) side of the joint.
- plication (tightening) of the tissue, which will
hold the great toe in a neutral or straight position.
A cut is made in the base of the metatarsal bone so that the first
metatarsal can be shifted toward the second, correcting the angle
between the two. This cut is called an osteotomy, and it is fixed
with a screw. This operation can correct a more severe deformity
than is possible with the chevron procedure.
The Arthrodesis Procedure
An arthrodesis is a procedure that corrects the deformity
of the toe, but eliminates motion in the metatarsophalangeal joint.
It is generally used for those with advanced arthritis in the joint
when a joint-sparing operation cannot be performed. In this operation,
the articular cartilage is removed from the arthritic joint and the
two surfaces of cut bone are fixed to each other with a screw and
a plate. Although this causes the joint to lose its motion, the deformity
is corrected and pain is eliminated.
What types of complications may occur?
The complication rate for bunion surgery is approximately 10%. These
complications include:
- An under correction or over correction (hallux varus)
can occur.
- The deformity can return.
- Joint stiffness.
|