
 History
HistoryPatients with knee arthritis usually describe a gradual onset of knee pain, restricted motion and activities, and pain at rest. The physical examination
Findings of knee arthritis may include:
There is usually tenderness around
the inside and outside portions of the joint line.
It is important to distinguish knee arthritis from hip arthritis
or disc degeneration in the lumbar spine, since the symptoms are similar.
Diagnostic
test and imaging
Usually, plain X-rays will show the presence of arthritis and any
abnormalities in the alignment of the lower leg and changes in the
mechanical axis. MRI scanning is usually not necessary to diagnose
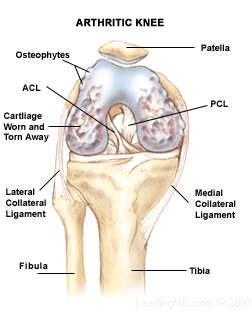
knee arthritis. There are four classic features of knee arthritis:
- Joint space narrowing
- Flattening of the femoral
condyle (the end of the femur)
- Subchondral sclerosis
(reactive bone thickening)
- Peripheral bone spur formation





