Labral Tears >> Diagnosis
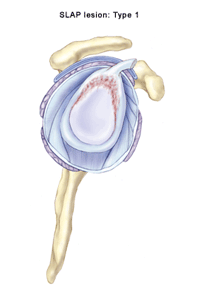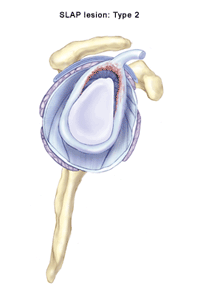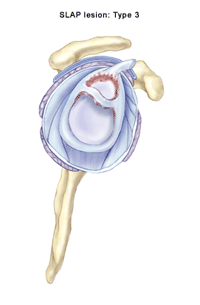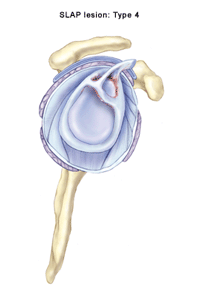 The
physician will first take a history of the patient's injury in order
to learn how it occurred. As mentioned earlier, the pain from a labral
tear is located at the site of the injury, and is usually referred
to as being deep inside the shoulder. A thorough physical exam may
reveal other sources of injury or another disorder. During a physical
examination of the shoulder:
The
physician will first take a history of the patient's injury in order
to learn how it occurred. As mentioned earlier, the pain from a labral
tear is located at the site of the injury, and is usually referred
to as being deep inside the shoulder. A thorough physical exam may
reveal other sources of injury or another disorder. During a physical
examination of the shoulder:
- the physician will measure motion to reveal any stiffness, which can be a sign of a labral tear.
- an instability exam will be performed.
- the O'Brien's test which focuses on the biceps and reveals pain, can help diagnose a labral tear.
The confirming test for a labral tear is an MRI preceded by an arthrogram. This procedure greatly enhances the diagnostic accuracy by allowing tears of the labrum to be seen more clearly.